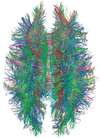
Diffusion Weighted
The magnitude of water signal attenuation on diffusion-weighted images depends on two factors: the translational movement of water molecules, and the amount of diffusion weighting. The latter varies according to the strength, duration, and separation time of the gradient pulses. The sensitivity to water diffusion is defined by the gradient factor b (sec/mm2). The higher the b values, the better the sensitivity of diffusion weighted imaging (usually three to four b values are used in diffussion-weighted sequences b50, b500, b1000 and b1400).
Beside the diffusion-weighted row data images, there is one more way to present diffusion data which is called the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map of water. These are calculated from diffusion-weighted images after the acquisition.
Use
Very useful for Diffusion-weighted whole-body cancer screening
Very useful for brain imaging
Very useful for cholesteatoma imaging
Very useful for prostate imaging
Very useful for gynecology imaging
Very useful for breast imaging
Useful for anterior neck imaging
Useful for small bowel imaging
Useful liver imaging
Useful for spine imaging
Useful for sacroiliac joint imaging
2. Sequence: Apparent diffusion coefficient
Abbr.: ADC
Physics: Reduced T2 weighting by taking multiple conventional DWI images with different DWI weighting, and the change corresponds to diffusion.
Main Clinical distinctions: Low signal minutes after cerebral infarction (pictured).
3. Sequence: Diffusion tensor